Logical Schema Design
From an SQL user's point of view, Vertica supports the standard relational data model, in which a schema consists of a collection of tables, each with a collection of columns (attributes) and rows (tuples), and other SQL objects.
Vertica does not support standard SQL views (stored queries). Instead, it provides  projections, which are entirely transparent to SQL users other than the database administrator. These are discussed in the Projections section of this document.
projections, which are entirely transparent to SQL users other than the database administrator. These are discussed in the Projections section of this document.
A projection is a special case of a  materialized view that provides physical storage for data. A projection can contain some or all of the columns of one or more tables. A projection that contains all of the columns of a table is called a
materialized view that provides physical storage for data. A projection can contain some or all of the columns of one or more tables. A projection that contains all of the columns of a table is called a  superprojection. A projection that joins one or more tables is called a pre-join projection. Most projections are used for ad-hoc query processing and K-safety but it is possible to have query-specific projections.
superprojection. A projection that joins one or more tables is called a pre-join projection. Most projections are used for ad-hoc query processing and K-safety but it is possible to have query-specific projections.
A superprojection is a projection that contains every column of a table in the Logical Schema. A table can have multiple superprojections with different sort orders.
A materialized view is similar to a standard SQL view with one major exception: the data is actually stored on disk rather than computed each time the view is used in a query. A materialized view, then, must be refreshed whenever the data in the underlying tables is changed. A projection is a special case of a materialized view.
As in most relational systems, specific columns in Vertica tables can be designated as a primary key, or as a foreign key that references a primary key in another table. The tables in a Vertica database are assumed to obey the Dimensional Modeling concepts of a star schema or snowflake schema design. These are typical schema designs used in data warehouses.
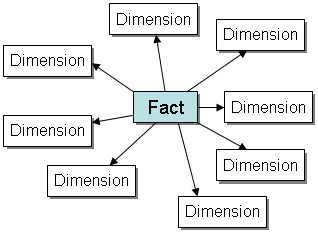
Star Schema
The star schema (sometimes called a star join schema) is the simplest  data warehouse schema. In a star schema design there is a central fact table with a large number of tuples, optionally surrounded by a collection of dimension tables, each with a lesser number of tuples. Every dimension table participates in a 1::n join with the fact table.
data warehouse schema. In a star schema design there is a central fact table with a large number of tuples, optionally surrounded by a collection of dimension tables, each with a lesser number of tuples. Every dimension table participates in a 1::n join with the fact table.
A data warehouse is a relational database that is designed for query and analysis rather than transaction processing. Data warehouses:
- are often subjected to a heavy load of periodic and ad-hoc queries.
- contain historical information that enables analysis of correlations and trends over long periods of time.
- integrate data from various production (transactional) databases. Extraction, transformation, and loading (
 ETL) software converts the data to a common format and copies it into a data warehouse at regular intervals.
ETL) software converts the data to a common format and copies it into a data warehouse at regular intervals. ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is a process in data warehousing that involves extracting data from outside sources, transforming it to fit a specific schema, and ultimately loading it into the database.
- typically consist of one or more star or snowflake schemas.
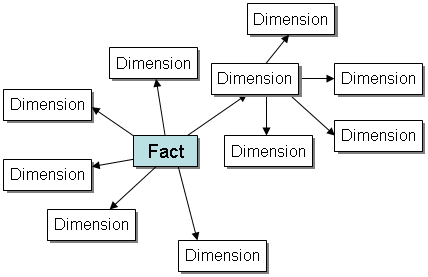
Snowflake Schema
A snowflake schema is the same as a star schema except that a dimension table can be normalized (hierarchically decomposed) into additional dimension tables. Every dimension table participates in a 1::n join with the fact table or another dimension table.
 projections, which are entirely transparent to SQL users other than the database administrator. These are discussed in the Projections section of this document.
projections, which are entirely transparent to SQL users other than the database administrator. These are discussed in the Projections section of this document. data warehouse schema. In a star schema design there is a central fact table with a large number of tuples, optionally surrounded by a collection of dimension tables, each with a lesser number of tuples. Every dimension table participates in a 1::n join with the fact table.
data warehouse schema. In a star schema design there is a central fact table with a large number of tuples, optionally surrounded by a collection of dimension tables, each with a lesser number of tuples. Every dimension table participates in a 1::n join with the fact table.
